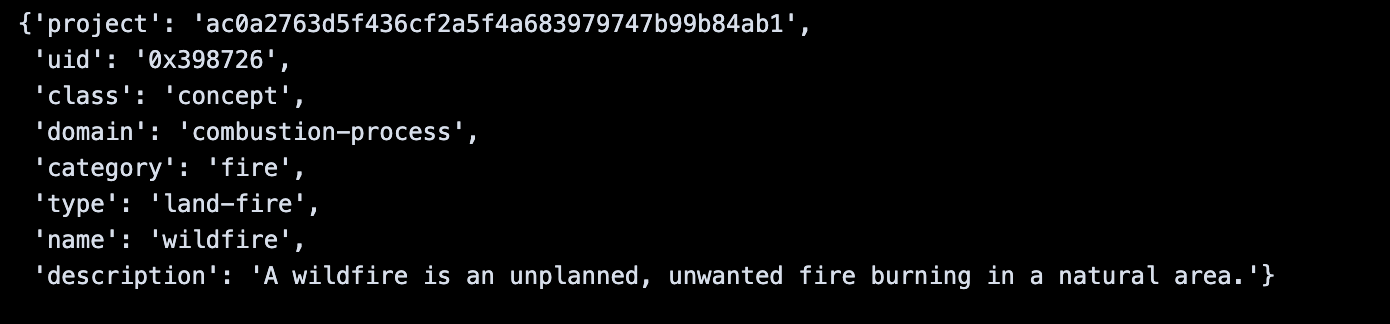
Create Concept Object
A geodesic.entanglement.object.object.Concept object can be thought of as an abstract idea, not a physical entity. In this example, we are going to create a 'wildfire' concept object and add it to the entanglement graph in a personal project.
All geodesic.entanglement.object.Object can have additional qualifiers;
however, only name is required. In this example we will also be adding the domain, category,
and type qualifiers and the description attribute.
Setup
Start by setting your active project.
import geodesic
geodesic.set_active_project('tutorials')
Creating The Object
concept_object = geodesic.entanglement.Object(
object_class='concept',
domain = 'combustion-process',
category = 'fire',
name='wildfire',
type='land-fire',
description='A wildfire is an unplanned, unwanted fire burning in a natural area.'
)
geodesic.entanglement.add_objects([concept_object], project='tutorials', overwrite=True)
concept_object.save()
The domain, category, and type qualifiers are used to help organize and classify the object.
The description attribute is optional and can be used to store additional information about the
object.
Accessing the Object
To check that your object has been created and added to the entanglement graph, you can use the
geodesic.entanglement.object.Object.get_objects method to search either by object type or by name.
geodesic.get_objects(object_class='concept')
[concept:combustion-process:fire:land-fire:wildfire]
geodesic.get_objects(search='wildfire')
[concept:combustion-process:fire:land-fire:wildfire]
We can save the search results as a list of
geodesic.entanglement.object.Objects and then access the object by index which will allow us to access the object's attributes.
obj_lst = geodesic.get_objects(search='wildfire')
wildfire_obj = obj_lst[0]
dict(wildfire_obj)