Create Observable Object
Problem
You want to create an geodesic.entanglement.object.object.Observable object and add it to the entanglement graph.
Solution
An geodesic.entanglement.object.object.Observable object is a physical property or attribute that can be observed by an
geodesic.entanglement.object.Object.Entity or
geodesic.entanglement.object.Object.Dataset.
geodesic.entanglement.object.object.Observabletypically denotes something measurable by a sensor or methodology.
In this example, we are going to create a geodesic.entanglement.object.object.Observable object for maximum fire radiative power band from the MODIS Terra Thermal Anomalies & Fire Daily Global. For details on adding the MODIS Terra Thermal Anomalies & Fire Daily Global dataset, refer to adding Google Earth Engine data set.
All geodesic.entanglement.object.Object can have additional qualifers,
though name is the only qualifier that is required. In this example, we will also be adding
domain, category, and type qualifiers, along with description and alias attributes.
Setup
Start by setting up the basic geodesic workflow in python.
>>> import geodesic
>>> geodesic.set_active_project('tutorials')
Creating The Object
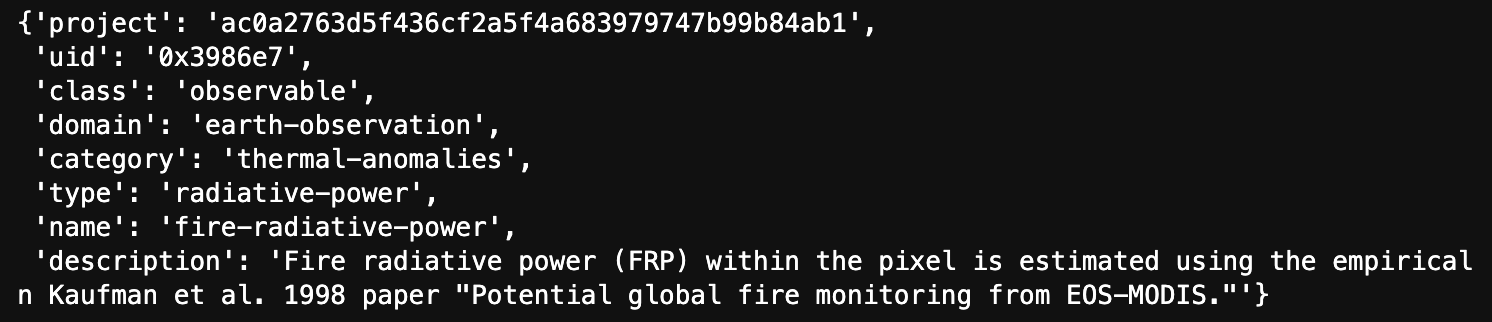
>>> observable_object = geodesic.entanglement.Object(object_class='observable',
name='fire-radiative-power,
domain = 'earth-observation',
category = 'thermal-anomalies',
type='radiative-power',
description = 'Fire radiative power (FRP) within the pixel is estimated using the empirical relationship established in Kaufman et al. 1998 paper "Potential global fire monitoring from EOS-MODIS."',
alias = 'Fire radiative power'
)
>>> observable_object.save()
The domain, category, and type qualifers are used to help organize and classify the object.
The description and alias attributes are optional and can be used to store additional
information about the object.
Accessing the Object
To check that your object has been created and added to the entanglement graph, you can use the
geodesic.entanglement.object.Object.get_objects method to search either by object type or by name.
>>> geodesic.get_objects(object_class='observable')
[observable:earth-observation:thermal-anomalies:radiative-power:fire-radiative-power]
>>> geodesic.get_objects(search='fire')
[observable:earth-observation:thermal-anomalies:radiative-power:fire-radiative-power]
We can save the search results as a list of
geodesic.entanglement.object.Objects and then access the object by index which will allow us to access the object's attributes.
>>> obj_lst = geodesic.get_objects(search='fire')
>>> fire_radiative_power_obj = obj_lst[0]
>>> dict(fire_radiative_power_obj)