Create Entity Object
Problem
You want to create an geodesic.entanglement.object.object.Entity object and add it to the entanglement graph.
Solution
An geodesic.entanglement.object.object.Entity object can represent a person, place or thing. In this example we are going to create a 'place' object for Carbon County in Wyoming and add it to the entanglement graph in a personal project.
All geodesic.entanglement.object.Object can have additional qualifers;
however, only name is required. In this example we will also add a domain, category, and
type qualifers, along with description, geometry, and item attributes.
Setup
Start by seting up the basic geodesic workflow in python.
import geodesic
geodesic.set_active_project('tutorials')
Creating The Object
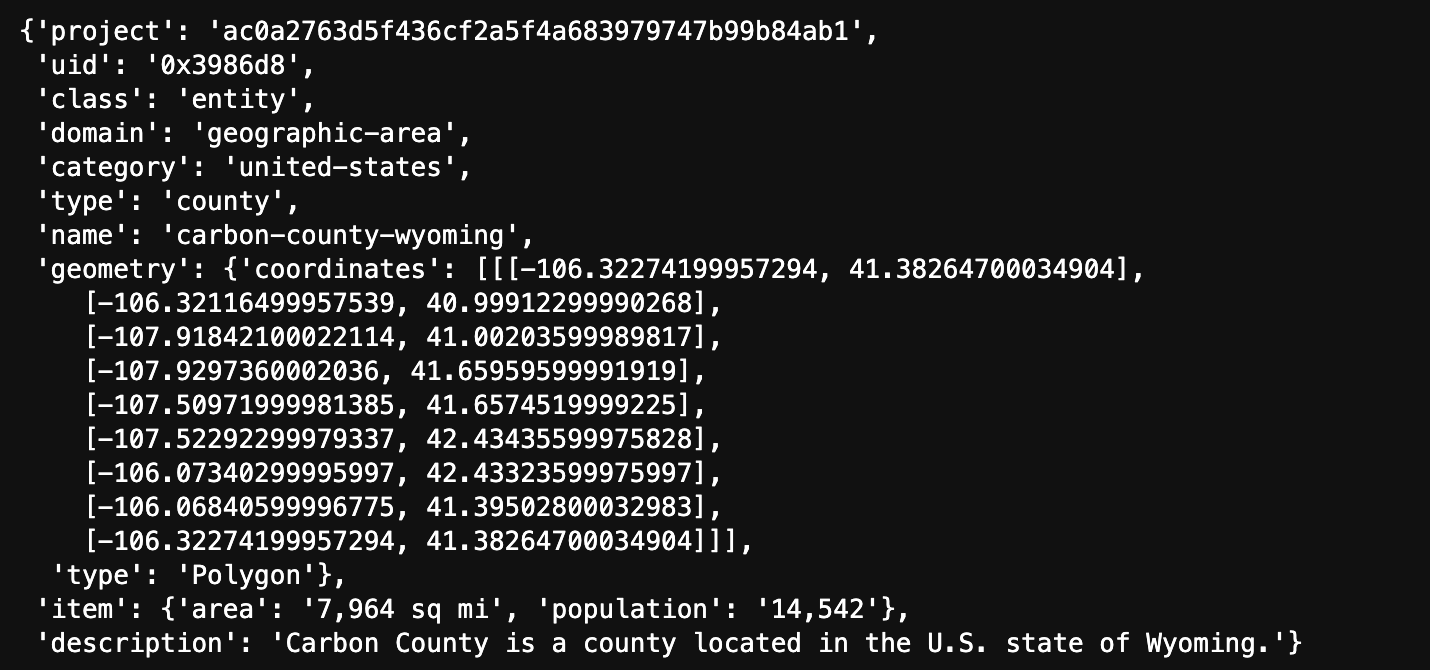
entity_object = geodesic.entanglement.Object(object_class='entity',
name='carbon-county-wyoming',
domain = 'geographic-area',
category = 'united-states',
alias='Carbon County, Wyoming',
type='county',
description='Carbon County is a county located in the U.S. state of Wyoming.',
geometry='POLYGON ((-106.32274199957294 41.38264700034904, -106.32116499957539 40.99912299990268, -107.91842100022114 41.00203599989817, -107.9297360002036 41.65959599991919, -107.50971999981385 41.6574519999225, -107.52292299979337 42.43435599975828, -106.07340299995997 42.43323599975997, -106.06840599996775 41.39502800032983, -106.32274199957294 41.38264700034904))',
item={'population': '14,542', 'area': '7,964 sq mi'}
)
entity_object.save()
The domain, category, and type qualifers are used to help organize and classify the object.
The description, geometry, and item attributes are optional and can be used to store
additional information about the object.
The geometry attribute can be anything, but only points/polygons will be indexed.
The item is an arbitrary dictionary of info about the object, however it must be JSON
serializable.
Accessing the Object
To check that your object has been created and added to the entanglement graph, you can use the
geodesic.entanglement.object.get_objects method to search either by object type or by name.
geodesic.get_objects(object_class='entity')
[entity:geographic-area:united-states:county:carbon-county-wyoming]
geodesic.get_objects(search='carbon')
[entity:geographic-area:united-states:county:carbon-county-wyoming]
We can save the search results as a list of
geodesic.entanglement.object.Objects and then access the object by index which will allow us to access the object's attributes.
obj_lst = geodesic.get_objects(search='carbon')
carbon_county_obj = obj_lst[0]
dict(carbon_county_obj)
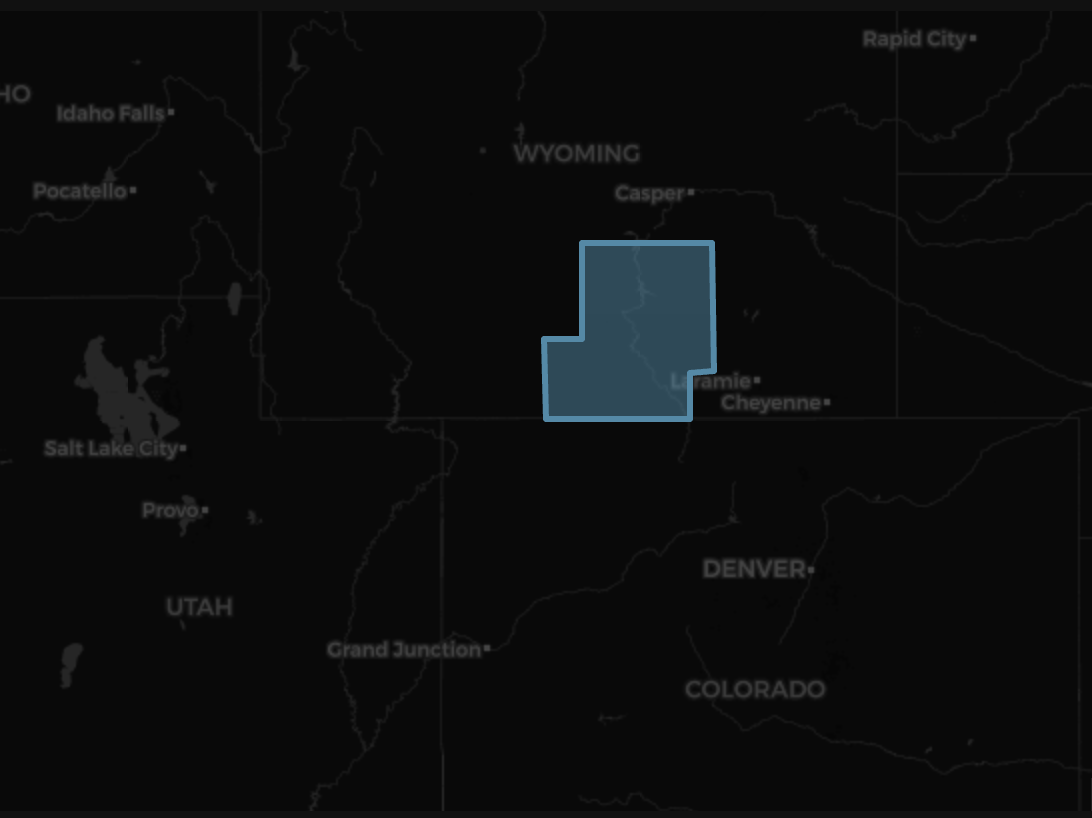
Mapping The Object
Since our geodesic.entanglement.object.object.Entity object has a geometry attribute, we can place it on a map. The method
geodesic.entanglement.object.Object.geometry will return the object's geometry which we can then create a feature collection and add it to a map.
from geodesic import mapping
fc = geodesic.Feature(geometry=carbon_county_obj.geometry)
m = mapping.Map(center=(41.067292, -105.948662), zoom=6)
m.add_feature_collection('carbon_county', fc)
m